The Definitive Guide to Wholesale Energy: How It Works, Prices & More
If you're searching for the best energy deals, it can be helpful to understand the wholesale energy market. The energy market can be a complicated business. But knowing how it works can help you save money.
In this guide, we explain what the wholesale energy prices are. We'll also cover how the wholesale market works and how it affects your bill.
Contents
- What Are Wholesale Energy Prices in 2025?
- How Have Wholesale Energy Prices Changed Over Time?
- What Is Wholesale Energy?
- How Does the Wholesale Energy Market Work?
- Who Produces the UK’s Wholesale Energy in 2025?
- What is the Fuel Mix of Wholesale Energy in the UK in 2025?
- How Does the Wholesale Market Affect My Energy Prices?
- What Affects Wholesale Energy Prices?
- Should You Switch Energy Suppliers?
What Are Wholesale Energy Prices in 2025?
According to the latest statistics in 2025, the most recent wholesale electricity prices are 4.28 pence per kWh. Natural gas wholesale recent prices are 4.20 pence per kWh. Wholesale gas and electricity prices started to increase in February 2024.
Prices have been slightly increases, although they remain below their like-for-like 2020-2023 levels. Here’s how the UK’s wholesale electricity and wholesale gas prices have changed throughout 2024-2025.
Data source: OFGEM
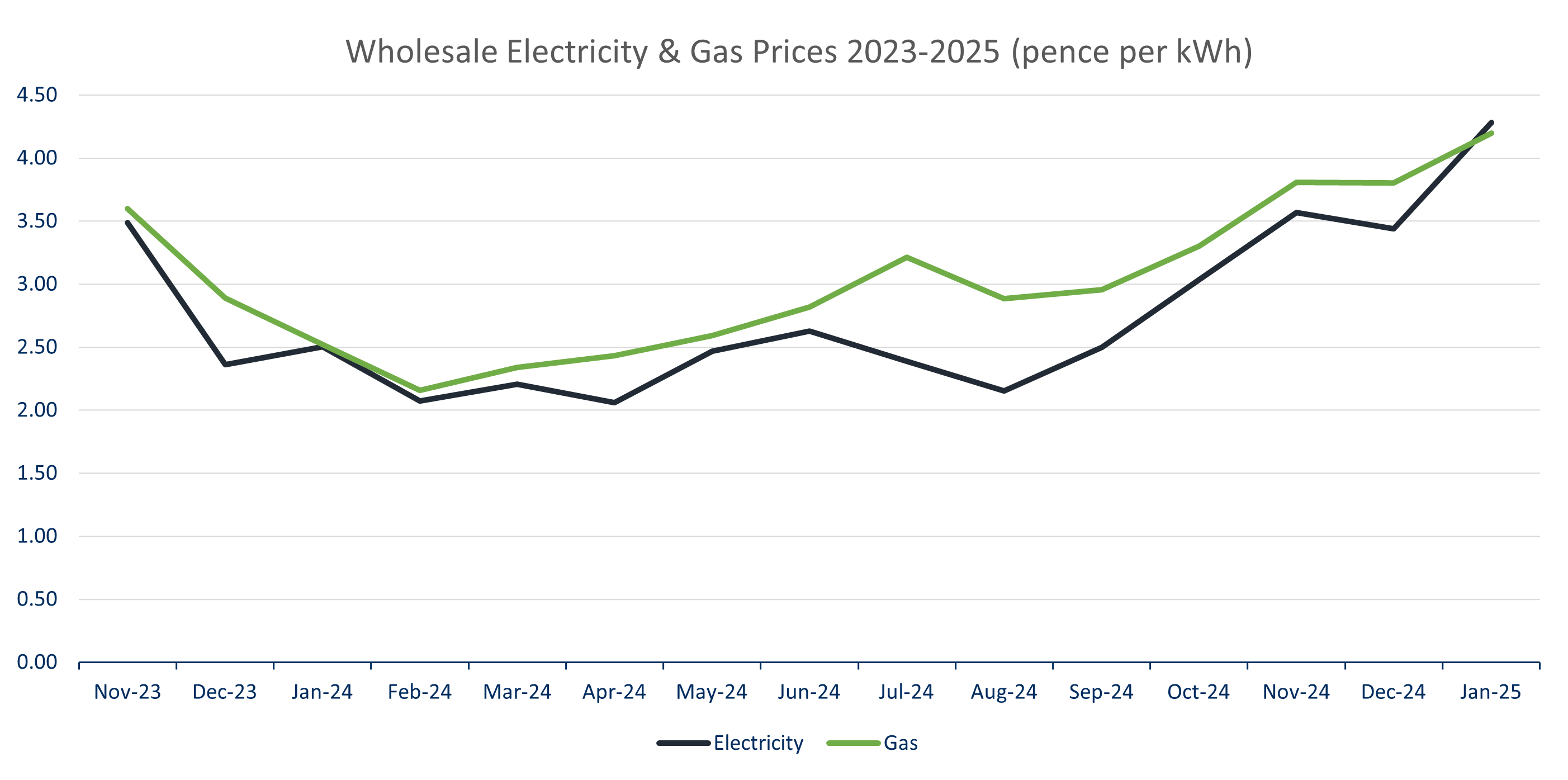
How Have Wholesale Energy Prices Changed Over Time?
In late 2021, energy prices rose rapidly due to the energy crisis that had developed as a result of demand and geo-political events. The winter of 2021 saw higher demand across Europe which was compounded by a lack of supply caused by European countries importing less gas from Russia, due to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
The result was that wholesale energy prices quickly escalated to 50p per kWh for electricity and 60p per kWh for gas. And it took all of 2023 for these prices to ease. In 2025, the market calmed significantly due to lower Summer demand and supply issues have had time to be addressed.
A forecast set by Cornwall Insights showed a fall of around £270 or 14% in Q2 of 2024. Price cap forecasts remain uncertain so there is no guarantee that prices will fall by much, despite being lower than they previously were.
Compare Business Electricity & Gas Tariffs
Get a comparison and start saving now
What Is Wholesale Energy?
Wholesale energy is electricity or gas that is purchased in bulk to resell for profit. Energy suppliers buy wholesale energy from energy producers. They will then add charges to cover the cost of distributing energy to you in the form of the domestic energy or business energy you use every day.
Other parties that purchase energy wholesale include:
- Financial intermediaries
- Energy traders
- Large energy consumers (such as multi-national corporations or those on a half hourly meter)
How Does the Wholesale Energy Market Work?
The wholesale energy market allows suppliers to buy and sell large quantities of energy to and from one another. In today’s market, smaller independent energy producers are also able to take part. This is stimulating the growth of new energy companies.
Since energy markets deregulated, end-users have benefited from:
- More reliable service
- More efficient transmission of energy
- Better price transparency from suppliers
Who Produces the UK’s Wholesale Energy in 2025?
The UK’s electricity and gas providers that generate electricity and source gas are as diverse as the UK’s energy suppliers that sell it to end users in the domestic and commercial segments.
That being said, 10 companies generate about three-quarters of the UK’s electricity and distribute it to the UK’s GB National Transmission System. We’ve compiled their market share in the table below - although this doesn’t include electricity imported from abroad.
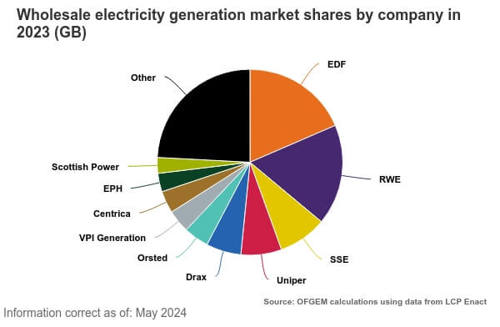
Source: OFGEM 2023 data (latest available in 2024)
Here’s the breakdown:
|
Company |
Market Share |
|
EDF |
18.29 |
|
RWE |
16.57 |
|
SSE |
7.83 |
|
Orsted |
6.26 |
|
EPH |
4.98 |
|
VPI Generation Limited |
4.64 |
|
Uniper |
4.58 |
|
Scottish Power |
4.07 |
|
Drax |
3.54 |
|
Triton Power |
1.93 |
|
Others |
19.1 |
What is the Fuel Mix of Wholesale Energy in the UK in 2025?
The electricity that lights our homes and powers our work spreadsheets comes from a wide range of fuels - known as the fuel mix. Although these fuels produce electricity that is pooled into the electricity grid, energy suppliers can choose what fuels generate the electricity they sell us, so when switching to an energy supplier, if the environment is on your mind, check our supplier pages for each supplier’s fuel mix to see if the supplier is right for you.
According to the most recent data, the UK’s fuel mix for electricity looked like this:
|
Fuel |
2022 (TWh/year) |
Share of Electricity Generation |
|
Gas |
122.69 |
40% |
|
Wind and Solar |
94.08 |
31% |
|
Nuclear |
43.35 |
14% |
|
Bioenergy |
31.51 |
10% |
|
Other fuels |
7.83 |
3% |
|
Hydro (natural flow) |
5.28 |
2% |
|
Coal |
5.11 |
2% |
|
Oil |
1.94 |
1% |
|
Pumped storage (net supply) |
-0.62 |
0% |
|
Net imports (Interconnectors) |
-5.34 |
-2% |
Source: OFGEM
But the fuel mix has not always been like this. In the last 10 years, renewable energy has become a larger and larger piece of the UK’s energy mix - and that is only set to increase with time. In fact, we’ve crunched the numbers, and in 2012 renewable electricity made up just 13% of the UK’s electricity fuel mix. In the final quarter of 2022, when the latest OFGEM data is available, that increased to 46% share.

Source: OFGEM
This growth in renewable electricity comes from both an increased investment into mostly solar and wind electricity generation, and a markedly decreased reliance on coal. While that is good news for the environment: coal is the highest CO2 emitter of the non-renewable fuels for generating electricity emitting 1,016 tonnes of carbon dioxide per GWh of electricity supplied, twice as high as for electricity supplied by gas (489 tonnes of carbon dioxide per GWh), according to Government figures, however gas as fuel for generating electricity has actually increased from 26% in Q4 2012 to 38% in Q4 2022.

Source: OFGEM
How Does the Wholesale Market Affect My Energy Prices?
Changes in the wholesale energy market can impact your bills. Any changes will depend on the type of energy tariff you’re on. Changes in wholesale prices can affect variable rate tariffs. Your prices may rise if the market becomes less competitive.
Fixed-rate tariffs will not be affected by wholesale changes. Your unit rate will be locked in for the duration of your contract. Wholesale energy prices make up almost half of your bill. Here, you can find a breakdown of your energy bill is calculated.

Wholesale price (42%)
Just under half of your electricity bill covers the wholesale price of energy.
Distribution (16%)
Retailers add a charge to your bill to cover the cost of getting energy to your property.
Taxes (24%)
Electricity is taxed highly if it’s not from a sustainable source. Taxes can add up to almost a quarter of your bill.
Operating costs (11%)
This part of your bill goes towards paying your suppliers' operating costs. They include salaries, research, and technology.
Profits (7%)
The last part of your bill makes up the profit that a supplier will make by selling you an energy tariff.
What Affects Wholesale Energy Prices?
Like any product, energy is subject to changes in supply and demand. Suppliers buy much of the energy we use in advance. Energy bought in advance is often sold at different prices. This is known as hedging.
Hedging allows energy companies to reduce changes in the price of gas and electricity. The practice protects you from big jumps in your energy bills. But what causes these changes in wholesale energy prices? Below are some of the factors that drive prices up and down.
Gas supply
At one time, the UK generated all its own gas needs. However the North Sea reserves have diminished in recent years. To keep an adequate gas supply, the UK now imports large amounts of natural gas. As a result, it must pay as much as EU countries to secure gas through European pipelines.
Relying on the EU means the UK is exposed to European gas shortages. When pipelines or gas fields in Europe go offline, gas prices for the continent spike.
Sustainability of the energy source
For the first time in 2019, renewable energy provided power to more properties than fossil fuel energy sources. This trend looks likely to continue given the government’s commitment to seeking a low-carbon economy.
Renewable energy is sustainable. Many hope it will stabilise energy markets as well as be better for the environment.
Changes in currency value
Wholesale energy prices are also influenced by the Pound’s strength against the Euro. When the Pound is stronger, gas and electricity prices fall. When the Euro is stronger, the prices the UK pays will increase.
Temperature
A lot of energy is used for heating. So, when temperatures are higher, demand goes down. This reduces the cost of wholesale energy. These prices are often linked to forecasts as wholesale energy is bought in advance.
Carbon tax
Energy providers have been pushed to meet carbon emissions targets. Charges are applied to companies based on the amount of carbon dioxide they use. Energy suppliers that fall behind carbon targets will need to pay a higher price. These increases can harm the broader market by encouraging increases in selling prices.
Global Events
The wholesale energy market is often affected by global events. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic initially reduced global wholesale prices.
However, conflicts or natural disasters in countries which produce gas or oil can increase wholesale energy prices around the world. UK markets are vulnerable to these changes because they are so reliant on imports. This has been seen with the rapid rise in wholesale energy prices as a result of the conflict in Ukraine.
Should You Switch Energy Suppliers?
Even if you’re not directly affected by wholesale costs, it’s always worth comparing energy prices. Some energy suppliers make better strategic purchases than others. That can trickle down to allow suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
If you’re on a variable rate tariff, you should monitor your unit rates. If your prices increase, you may be able to switch to a cheaper deal.
With Love Energy Savings, you can quickly compare a wide range of energy suppliers. All we ask for is your address and a few contact details. You can then compare the best energy deals online. To find out how much you could save, complete our online energy comparison calculator.
Wholesale Energy FAQs
-
Why are gas prices rising?
Rising gas prices in 2024 & 2025 are a result of a cold winter across Europe last year that has placed pressure on the gas supply and international climate affairs.
-
Does the wholesale market affect renewable sources?
When markets change significantly it usually places stress on other parts of the industry.
With a higher demand for to gas and electricity, the wholesale cost of renewable energy will also increase. The closer the UK moves towards low-carbon heating and starts to generate electricity, the less reliant we are on the wholesale market and less venerable to prices changes.
Ready to Start Your Energy Switch?
